What really happened to the complex societies of the Bronze Age? This question has stoked the fires of our curiosity for generations. We stand on the edge of history, peering into the abyss of time, trying to grasp what caused such advanced cultures to disintegrate almost simultaneously.
Imagine a world thriving with trade, art, and innovation, only to crumble into dust and mystery. Such was the fate of various civilizations during what we call the Bronze Age Collapse.
The answer isn't easy or straightforward; it seems like a puzzle missing half its pieces. Several factors likely converged, leading to this widespread societal breakdown.
Some scholars point towards natural disasters that may have devastated crops and economies. Others suggest invaders known as "Sea People" played a significant part in dismantling established powers through war.
Perhaps internal social strife grew too heavy for these civilizations to bear, or trade routes collapsing under external pressures choked essential supply lines. The theories are many and complex as we piece together clues from ancient ruins and scattered texts.
Unraveling the Mystery: What Was The Bronze Age Collapse?
As we turn the dusty pages of ancient history, there is one chapter that continues to intrigue us deeply: the Bronze Age Collapse. The question of what led to the downfall of flourishing civilizations during this era remains shrouded in mystery, even thousands of years later.

Our quest takes us back over three millennia, to a time when bronze was more than just a metal, it was the backbone of society's tools, weapons, and artwork. Suddenly though, between 1200 and 1150 BCE, something catastrophic happened that swept across the lands bordering the Mediterranean Sea.
Mighty empires crumbled almost simultaneously, economies shattered like glass underfoot, and cultures were lost in time's relentless march. But what could have caused such monumental societal disintegration? That’s what draws us in as we attempt to unravel this perplexing event known as the Bronze Age CollaApse.
Understanding the Bronze Age Collapse
When we talk about the Bronze Age Collapse, we’re looking at one of history's greatest puzzles. It all happened over 3,000 years ago, at a time when people were making amazing things out of bronze.
This period was full of rich cultures and busy cities. But suddenly, almost like a row of dominoes crashing down, these great civilizations around the Mediterranean began to fall apart.
Why is it called a collapse? Well, imagine the putty that holds things together starts melting away; everything touches comes unstuck. That's what seemed to happen to societies during this dark moment. Cities were destroyed and abandoned; trading stopped; knowledge was lost; and writing nearly disappeared from some areas.
So why did it happen? There are many guesses but no sure answers — that’s why it’s still such a big question for us today. What we do know is this: Around 1200 BCE, big names like the Hittites in modern-day Turkey, Mycenaean Greeks, and even Egypt felt this sudden shockwave.
Each place found itself facing hard times as warriors stopped fighting their wars with chariots as they used to do. Farmers could not grow crops like before which led to hungry people — lots of them! And leaders who were once powerful now had less control over their lands.
But get this: It wasn’t just one problem that brought them all down but likely a mix of issues coming together at a most unlucky time for these ancient folks.
So here we are now trying our best to piece together this old mystery from bits left behind – broken pots, ruins deep under dirt today or stories written on clay tablets long ago waiting for keen eyes to read them again after so much time has passed.
Also Read: Spanish Inquisition: Secrets and Historical Insights
Evaluating Theories Behind The Demise Of An Era
A myriad of theories have been put forward to explain this sudden disappearance, each pointing toward different factors that may have led to the widespread disintegration of these ancient societies.

From environmental changes to foreign invasions, and economic turmoil to technological shifts, experts are piecing together evidence in an attempt to solve this historical puzzle.
Let us evaluate these theories, considering not just individual possibilities but also how they might intersect and contribute collectively to one of history's greatest tales of societal upheaval.
Unveiling 5 Leading Theories About The Bronze Age Collapse
Several theories have been proposed to explain this mysterious downfall, and each gives us fascinating insights into how complex and vulnerable ancient civilizations might have been.
- Natural Disasters Theory: Some researchers believe that a string of natural calamities struck the Mediterranean region, which could have included droughts, famines, or earthquakes. These disasters would have stressed the societies of the time beyond their capacity to cope.
- The Sea People Invasion Theory: Accounts from ancient Egypt reference enigmatic aggressors known as 'The Sea People.' It's thought that these maritime raiders attacked and pillaged cities throughout the Mediterranean, sparking widespread turmoil.
- Economic Breakdown Theory: Trade networks were crucial for Bronze Age economies. Some scholars suggest that interruptions in trade routes led to economic collapse in several interconnected civilizations.
- Internal Rebellions and Political Collapse Theory: Power struggles and societal rifts could have weakened states internally at a critical time when external threats were also escalating, leading to a rapid breakdown of political structures.
- Technological Advancement and Warfare Theory: With advancements in iron forging surpassing bronze weapons' superior strength and availability may have allowed smaller groups to challenge established powers effectively.
Figuring out exactly why these once-prosperous civilizations fell has challenged historians for decades; perhaps it wasn’t just one single cause but a combination that together sparked this widespread collapse.
Deciphering Signals From Ancient Ruins And Texts
To piece together what happened during the Bronze Age Collapse, archaeologists turn detective – sifting through ruins and deciphering old texts for clues:
- Ancient Ruins Analysis:
Ruins are like snapshots of civilization's last moments before their abrupt end—burnt layers within city remains can point to warfare or natural disaster events such as earthquakes or wildfires. - Interpreting Inscriptions:
Texts from the era can offer tantalizing hints about what people experienced during those times—references to invasions or descriptions of famine conditions provide key context as analysts try to recreate historical narratives. - Cross-disciplinary Studies:
Archaeologists often work alongside geologists, climate scientists, and historians who specialize in different regions' histories so they can better understand how broader patterns may have influenced specific areas under scrutiny during the late Bronze Age period. - Data Synthesis from Diverse Sites:
By comparing evidence across various sites experiencing simultaneous upheaval—a global picture begins taking shape revealing possible interconnected chains of cause-and-effect spanning continents.
Through such careful examination, researchers hope not just to outline probable scenarios but also gain insight into how ancient populations may have adapted—or failed—to survive stressors akin to those our modern world faces today.
Also Read: Pax Romana: Exploring the Era of Peace
Contenders For Catastrophe
Unraveling this mystery takes us through a labyrinth of theories and speculations, each vying for credibility as the contender for this widespread catastrophe.

We've set our sights on dissecting these key suspects, probing remnants of a bygone age to reveal their possible roles in scripting one of history's most perplexing finales, the collapse that rewrote the fate of entire civilizations around the Mediterranean basin.
Join us on this investigative journey as we scrutinize five leading explanations that stand testament to human resilience amid trials by nature, war, and intricate societal weaves.
1. The Sea People Invasion Theory
One of the most talked-about theories we explore is the Sea People Invasion Theory. Who were these mysterious "Sea People"? They appear in ancient texts as a confederation of naval raiders who wrought chaos upon the civilizations along the Mediterranean shores.
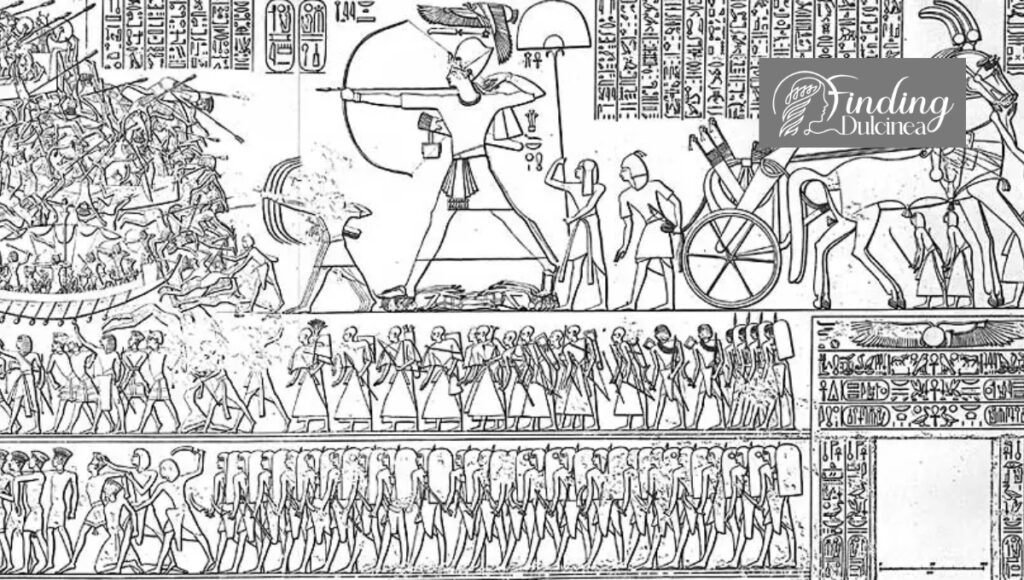
We debate their shadowy origins and piecemeal appearances in Egyptian and other records.
- Historical records: Our look into ancient texts, notably from Egypt, reveals mentions of battles against formidable groups collectively known as the Sea Peoples—a term coined by modern scholars.
- Archaeological evidence: We examine ruins and artifacts—destroyed cities and fortresses—which suggest widespread warfare and societal disruption during this particular time period.
- Cultural impact: The invasions are believed by some to have led to systemic collapses, not just through direct confrontation but also by disrupting trade networks vital for Bronze Age economies.
Their potential role in causing collapse sparks much debate among us because while there is evidence of their attacks, it is unclear if they were a cause or a symptom of wider societal disintegration.
2. Climate Catastrophe Hypothesis
When we look back at history, we often find clues that tell us big stories. One such tale comes from the time of the Bronze Age Collapse. Some folks think a climate disaster might be behind this big change in ancient times.

We call this idea the Climate Catastrophe Hypothesis. Now, let's take a closer look at what this means and how it could have shaken up old societies.
Here's how that might've happened:
- Years without Rain: Think of a time when rain doesn't come for years. That's what we call a drought. Ancient writings tell us about skies that didn't pour down water for too long. Scientists also find proof in the ground that the earth was very dry.
- Crops Could Not Grow: No rain means no water for plants. Without plants, there's not enough food. It makes sense that if this went on for a long time, people would have a tough time staying alive.
- People Move or Fight: Hunger can make people do desperate things. They might leave their homes to find food. Or they might fight their neighbors for what little they had. This sort of thing can break a society apart.
- The Domino Effect: Food is just the start. Trading depends on goods like food. Less food means less trade. When trade slows down, some jobs disappear. People lose ways to make a living.
- Evidence in Ice and Trees: We know about the weather back then because of clever science tricks. Researchers look at ice from mountains or rings inside old trees. These things keep records of what the climate was like.
So, could the Bronze Age Collapse be because of a big change in the weather? Some say yes. They think it was one main reason why those ancient people couldn't keep their way of life going.
Through our exploration, we link these environmental changes as possible catalysts for economic decline and social upheaval that preceded widespread societal collapse during the Bronze Age.
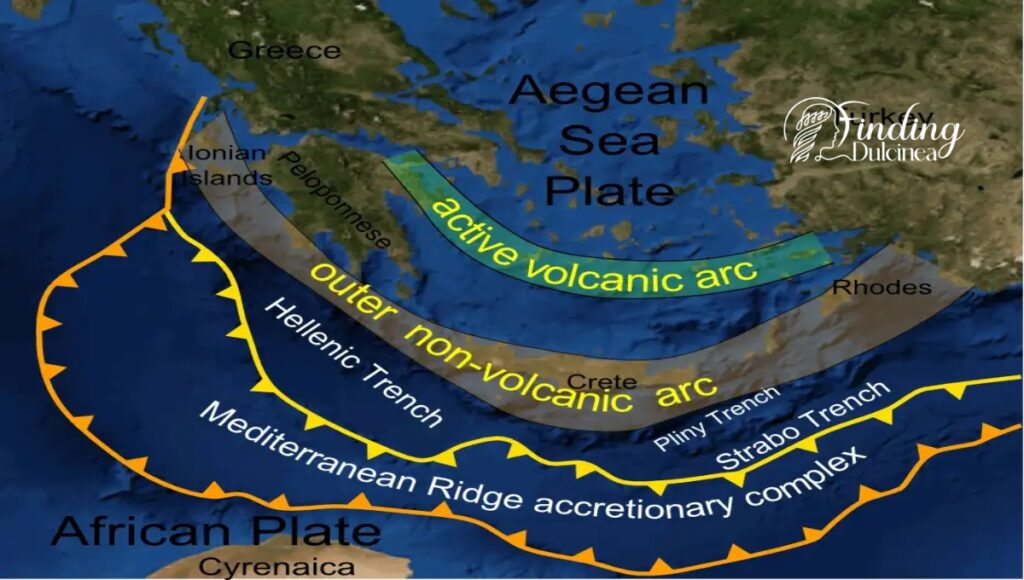
3. Ground Shaking Discoveries: Earthquakes' Impact on Civilizations
Some historians and archaeologists suggest that earthquakes could have played a crucial role in unsettling Bronze Age societies.
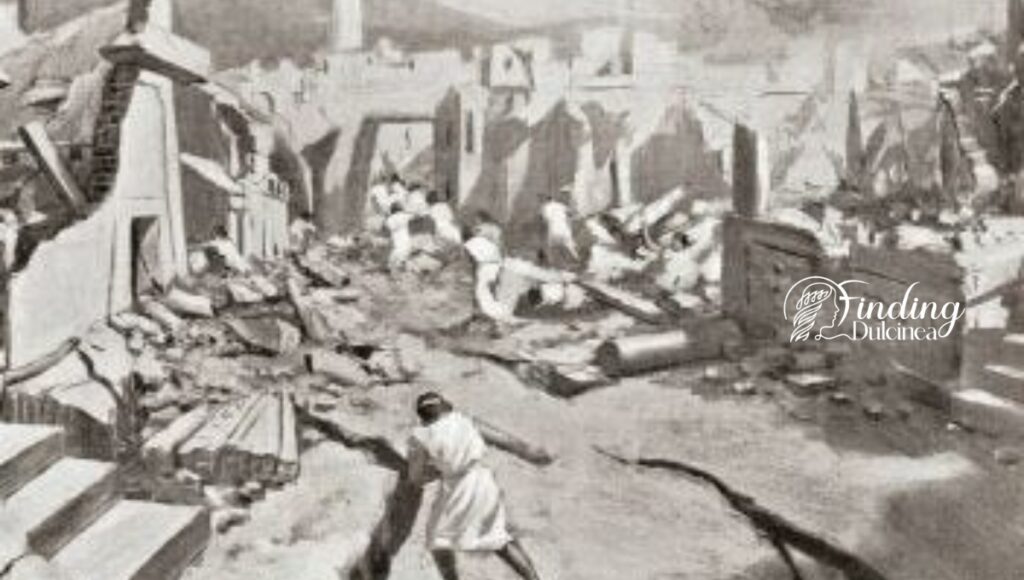

- Geologic layers: By scrutinizing soil stratification and fault lines, we find signs of frequent and severe earthquakes during the period in question.
- Archaeoseismology: Ancient destruction layers at various archaeological sites can be coincident with seismic events, offering a timeline that implicates earthquakes in the Bronze Age Collapse.
- Societal vulnerability: As sturdy as they seem, even stone-built cities would be devastated by powerful tremors. We propose that repeated seismic catastrophes could have undermined societies’ resilience, both structurally and economically.
Our analysis includes accounts from surviving texts referring to earth-shaking events and their destructive aftermaths which might signify an era more susceptible to nature's unrest than previously thought.
Also Read: Eva Perón: Argentina’s Iconic First Lady Activist
4. Warfare Revolution and Technological Advancements’ Role
Our explorations take us to a time marked by the clanging sounds of new metals and the sharp strategies that turned tides of war. The late Bronze Age saw a leap in military technology and combat tactics, movements that would forever alter the landscape of civilizations.
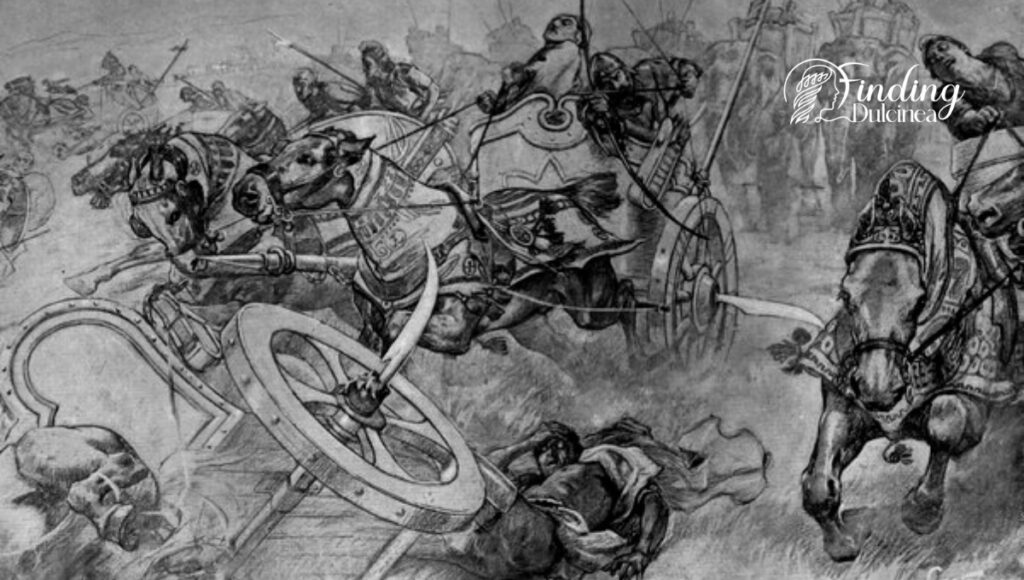

- Emergence of iron: We look at the transition from bronze to iron weapons—a technological shift that possibly rendered old defenses obsolete.
- New tactics: Besides improved armaments, changes in combat strategies are evident as well. The use of chariots and developments in fortifications may have shifted power dynamics dramatically.
- Political upheaval: We also explore how these advancements could exacerbate political instability. An arms race amongst competing powers sometimes leads to internal strife as much as it fends off external threats.
Together these factors paint a picture of a time when martial innovation may well have contributed significantly to collapses across late Bronze Age kingdoms.
5. Exploring the Systems Collapse Theory
The tale of our ancient past is full of mysteries, and one particular puzzle has intrigued us more than most: the vast and sudden downfall of entire civilizations during the Bronze Age Collapse. Among various interpretations lies a compelling notion known as the Systems Collapse Theory.
This theory proposes that it wasn't just one event but a chain reaction of failures in critical societal systems that led to this widespread ruin.
- Economic interdependence: The trade networks tying together different civilizations were complex; disruptions due to invasions or natural disasters had implications beyond local regions.
- Political instability chains: A single faltering state could send ripples through alliances and vassal relationships leading to wider crises.
- Cultural coalescence breakdowns: With widespread disruptions came the loss of shared ideologies that held communities together; these bonds are often underestimated until after they unravel through compounded stressors leading towards sociopolitical fragmentation.
Assessing this multifaceted theory involves acknowledging how interlinked communities might fail en masse when subjected to sustained pressures, both human-made and natural, which perhaps offers us an overarching lens through which we can understand this historical perplexity better.
Each theory brings its own set of evidence supporting why such thriving cultures could face sudden downturns but also leaves gaps urging further inquiry, a challenge we continue embracing eagerly as history enthusiasts piecing together ancient puzzles with modern insights.
Reassembling History Piece By Piece
Reassembling history, especially when it comes to vast societal upheavals like the Bronze Age Collapse, is akin to piecing together a millennia-old jigsaw puzzle. Each fragment uncovered from the soil, each character deciphered from a weathered inscription offers us a glimpse into our distant past.
As we delve into these ancient calamities with modern eyes, armed with contemporary technology and cross-disciplinary methodologies, we find ourselves stitching together narratives that were once lost to time.
But as we knit this historical tapestry using threads pulled from varied sources of insight, we must be cautious, the fabric of understanding is delicate and can be reshaped with each new discovery.
Interpreting Collapsed Civilizations With Modern Eyes
When we peer into the past, especially as far back as the late Bronze Age, our understanding is often shaped by the present. Modern interpretations have the power to breathe new life into ancient events, but they can also add layers of complexity and raise new questions.
As we grapple with the enigma of ancient civilization collapses, such as the Bronze Age Collapse, our perspectives are continuously refined through technological breakthroughs and interdisciplinary studies.
- Technological Advancements in Archaeology: In recent years, we've seen leaps in technology that allow us to uncover hidden details of collapsed civilizations. Satellite imagery can reveal lost cities buried under centuries of earth while ground-penetrating radar peels back layers without a single shovel strike. These technologies provide us with a non-invasive look at structures and layouts, letting us rebuild an image of societies in their prime before their untimely demise.
- Datasets Bigger Than Ever: Big data isn't just a buzzword for businesses; it's a bonanza for historians and archaeologists. Massive amounts of data from different sites can be cross-referenced to find patterns previously undetectable. Climate models constructed with this data might show periods of drought or natural disasters correlating closely with societal collapse timelines.
- Applying Interdisciplinary Approaches: By combining knowledge from varied disciplines like climatology, geology, anthropology, and even economics, we gain more comprehensive insights into what may have caused these civilizations to fail so suddenly. For example, economic theories help us understand trade disruptions while anthropological studies give clues about social upheaval following these disruptions.
- DNA Analysis Revolution: Advances in DNA analysis offer personal narratives within larger events like catastrophes or migrations due to collapses. We now know more about how populations moved and changed because genetic markers follow families across time and geography.
- Cultural Compilation through Literature Study: The study of ancient texts offers glimpses into day-to-day life during times that may lead to collapses. Translations continue to improve thanks to a better understanding of historical languages like those spoken by Jesus which illuminates nuances that once eluded researchers.
As historians and scientists fuse their expertise with state-of-the-art tech advancements to evaluate ancient ruins and texts afresh, interpretation becomes both clearer and more speculative amidst abundant information streams never available before.
Also Read: Socratic Paradox Explored: All I Know is That I Know Nothing
FAQs
What period did the Bronze Age cover?
The Bronze Age spanned from about 3300 to 1200 BCE, varying by region. It was a time when bronze was widely used for tools and weapons.
Why is understanding the bronze age collapse important for current societies?
Understanding the Bronze Age Collapse helps current societies learn from past societal failures, potentially offering insight into how to prevent similar downfalls today.
Can we see similarities between any current threats our civilization faces and those faced during the Bronze Age?
Yes, modern concerns like climate change, economic disruptions, and technological shifts mirror some factors that contributed to the Bronze Age Collapse.
Conclusion
As we reflect on our journey through the mysterious mists of time, exploring the theories surrounding the Bronze Age Collapse, it's clear that unraveling history's enigmas is a complex endeavor.
We've delved into various possibilities, from fantastical invasions by unknown marauders to natural disasters shaking the very foundation of ancient societies. Each theory stands as a testament to our relentless pursuit of knowledge and understanding of our past.
Anne Kostick has been Editor-in-Chief since September 2007. Previously, Anne was a principal at Foxpath IND, a publishing, consulting and editorial services company specializing in the transition to and from traditional content publishing and online content management, development and publishing. Her clients included trade book publishers, technology and financial services Web sites, and arts and cultural institutions. Previously, she worked as Licensing and Product Development Director, Senior Acquisitions Editor and Director of Electronic Publishing for Workman Publishing, and as Senior Acquisitions Editor for Harry N. Abrams/Stewart, Tabori & Chang. In the online world she worked as Director of Content Development for Vitaminshoppe.com. Anne has a B.A. in Greek and Latin, with a minor in Theater, from Beloit College. She is the author of several books for children, as well as a definitive collection of jokes.
